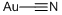Other grades of this product :
| GOLD(I) CYANIDE Basic information |
| GOLD(I) CYANIDE Chemical Properties |
| Provider | Language |
|
ALFA
| English |
| GOLD(I) CYANIDE Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | yellow powder(s); hexagonal; odorless; iridescent in sunlight; slowly decomposes in presence of moisture [MER06] | | Physical properties | Yellow hexagonal crystals; odorless; density 7.14 g/cm3; decomposes slowly in the presence of moisture or decomposes on heating; insoluble in water, alcohol and ether; also insoluble in dilute acids; soluble in aqueous solutions of potassium-, or sodium cyanide, ammonia, and aqua regia. | | Uses | Electrolyte in the electroplating industry | | Preparation | Gold(I) cyanide may be prepared by boiling sodium aurus cyanide, Na[Au(CN)2] with hydrochloric acid:Na[Au(CN)2] + HCl AuCN + HCN + NaClThe complex cyanide, Na[Au(CN)2] is made by dissolving gold in a dilute solution of sodium cyanide in the presence of air; or by dissolution of a gold anode in a solution of sodium cyanide during electrolysis. The solution is evaporated to separate the complex, Na[Au(CN)2], which is purified by recrystallization from water. Potassium cyanide may be used instead of sodium cyanide to prepare gold(I) cyanide. | | Hazard | Toxic material.
| | Purification Methods | The lemon yellow powder is sparingly soluble in H2O and EtOH but soluble in aqueous NH3. It is obtained by heating H[Au(CN)2] at 110o. Wash it well with H2O and EtOH and dry it at 110o. It has an IR band at max 2239 cm -1 typical for C stretching vibration. [Glemser & Sauer Handbook of Preparative Inorg anic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1064 1965.] CARE: may evolve HCN. |
| GOLD(I) CYANIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|