Other grades of this product :
| 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate Basic information |
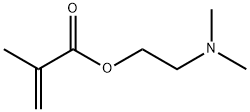
| Product Name: | 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate | | Synonyms: | DMAEMA N,N-Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate;2-(N,N-DIMETHYLAMINO)ETHYL METHACRYLATE;Ageflex fm-1;ageflexfm-1;beta-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate;beta-(N,N-Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate;beta-(n,n-dimethylamino)ethylmethacrylate;beta-dimethylaminoethylmethacrylate | | CAS: | 2867-47-2 | | MF: | C8H15NO2 | | MW: | 157.21 | | EINECS: | 220-688-8 | | Product Categories: | organic chemical | | Mol File: | 2867-47-2.mol |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | -50 °C | | Boiling point | 182-192 °C(lit.) | | density | 0.933 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | | vapor density | 5.4 (vs air) | | vapor pressure | <1 mm Hg ( 25 °C) | | refractive index | n20/D 1.439(lit.) | | Fp | 149 °F | | storage temp. | 2-8°C | | solubility | 500g/l soluble | | form | Liquid | | pka | 8.18±0.28(Predicted) | | color | Clear colorless Liquid | | explosive limit | 1.20%(V) | | Water Solubility | Less dense than water and insoluble in water. | | BRN | 1757048 | | Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing or reducing agents. May decompose on exposure to air and moisture. May undergo autopolymerization. Light sensitive. | | InChIKey | JKNCOURZONDCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | LogP | 1.13 at 25℃ | | CAS DataBase Reference | 2867-47-2(CAS DataBase Reference) | | NIST Chemistry Reference | Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate(2867-47-2) | | EPA Substance Registry System | 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate (2867-47-2) |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | colourless liquid | | Uses | N,N-Dimethylaminoethyl-methacrylate is an amine activator in visible-light-cured dental-acrylic composite materials. | | Uses | 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate is used in the synthesis of poly ((2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate), block copolymers of 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and n-butyl methacrylate and amphiphilic AB block copolymers of 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate. It is also used in the preparation of polymer. | | Uses | 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate may be used in:- the synthesis of poly ((2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)
- block copolymers of 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and n-butyl methacrylate
- amphiphilic AB block copolymers of 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate
| | General Description | A clear colorless liquid. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air and corrosive to eyes and mucous membranes. May polymerize exothermically if heated or contaminated. If polymerization takes place inside a closed container, the container may rupture violently. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Toxic by skin absorption, ingestion and inhalation. Used to make plastics and in textiles.
| | Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water. | | Reactivity Profile | 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate is both an amine and an ester. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. | | Health Hazard | TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. | | Fire Hazard | Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. May polymerize explosively when heated or involved in a fire. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form. | | Safety Profile | Poison by
intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by
ingestion and inhalation. A skin eye, and
mucous membrane irritant. A powerful
lachrymator. Flammable when exposed to
sparks, heat, open flame, or oxidizers. To
fight fire, use alcohol foam, dry chemical,
spray. When heated to decomposition it
emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also
ESTERS. |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|