Other grades of this product :
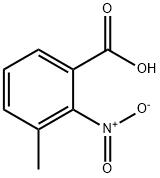
| 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid Basic information |
| 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 220-223 °C (lit.) | | Boiling point | 314.24°C (rough estimate) | | density | 1.4283 (rough estimate) | | refractive index | 1.5468 (estimate) | | storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature | | pka | 2.26±0.10(Predicted) | | form | powder to crystal | | color | White to Almost white | | Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 22 ºC | | BRN | 1960698 | | CAS DataBase Reference | 5437-38-7(CAS DataBase Reference) | | EPA Substance Registry System | 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid (5437-38-7) |
| 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | white to slightly yellow crystalline powder | | Uses | 2-Nitro-m-toluic Acid, is a building block used for the synthesis of various compounds. It can be used for the synthesis of novel Indolin-2-one derivatives as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. | | General Description | Prisms or white crystalline solid. | | Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water. | | Reactivity Profile | 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid is a nitrated carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. | | Fire Hazard | Information concerning the flash point of 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid is not available. 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid is probably combustible. | | Purification Methods | Recrystallise it from EtOH. The methyl ester has m 74o (from MeOH), and the amide [60310-07-8] M 180.1, has m 192o (needles from H2O, prisms from EtOH). [Beilstein 9 H 480, 9 IV 1722.] |
| 3-Methyl-2-nitrobenzoic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|