Other grades of this product :
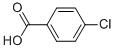
| 4-Chlorobenzoic acid Basic information |
| 4-Chlorobenzoic acid Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 238-241 °C(lit.) | | Boiling point | 274-276 °C | | density | 1.540 | | refractive index | 1.5812 (estimate) | | Fp | 238 °C | | storage temp. | room temp | | solubility | methanol: soluble1%, clear, colorless to faintly yellow | | form | Crystalline Powder | | pka | 3.98(at 25℃) | | color | White to yellow | | PH | 4.3 (0.08g/l, H2O, 20℃) | | Water Solubility | soluble in hot water | | λmax | 284nm(EtOH)(lit.) | | Merck | 14,2125 | | BRN | 907196 | | Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with bases, strong oxidizing agents. | | InChIKey | XRHGYUZYPHTUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | CAS DataBase Reference | 74-11-3(CAS DataBase Reference) | | NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzoic acid, 4-chloro-(74-11-3) | | EPA Substance Registry System | p-Chlorobenzoic acid (74-11-3) |
| 4-Chlorobenzoic acid Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | white to light yellow crystal powder. Soluble in methanol, anhydrous ethanol and ether, very slightly soluble in water, toluene and 95% ethanol. | | Uses | 4-Chlorobenzoic acid is a benzoic acid analogue that showed antifungal activity against strains of Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus terreus, causative agents of human aspergillosis, in in vitro bioas says. It is used as a preservative.P-chlorobenzoic acid is the intermediate of fungicide dimethomorph, rodenticide Warfarin, Coumatetralyl and insecticide flumethrin, and also the intermediate of dye and medicine. | | Uses | 4-Chlorobenzoic acid can be used:As a ligand to synthesize luminescent lanthanide complexes for bio-labeling or fiber communication applications.To prepare organotin(IV) chlorobenzoates exhibiting anticorrosion properties.As a ligand to synthesize di-n-butyl(4-chlorobenzoxy)(4-chlorobenzohydroxamato)tin(IV). | | Preparation | 4-Chlorobenzoic acid is obtained by oxidation of p-chlorotoluene: add potassium permanganate solution to the mixture of p-chlorotoluene and water in stages. The reaction is refluxed under stirring for 5-6h, then acidified with hydrochloric acid to pH 2, filtered to obtain the crude product, and recrystallized with ethanol to obtain the finished product. | | Definition | ChEBI: 4-chlorobenzoic acid is a monochlorobenzoic acid carrying a chloro substituent at position 4. It has a role as a bacterial xenobiotic metabolite. It derives from a benzoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a 4-chlorobenzoate. | | Synthesis Reference(s) | Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 2, p. 135, 1943Synthetic Communications, 25, p. 3695, 1995 DOI: 10.1080/00397919508015507Tetrahedron Letters, 22, p. 1013, 1981 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82853-7 | | General Description | Triclinic crystals or light fluffy white powder.4-Chlorobenzoic acid is a degradation product of indomethacin. It is degraded by Acinetobacter sp. strain ST-1 and causes its dehalogenation to yield 4-hydroxybenzoic acid under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. | | Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water. | | Reactivity Profile | 4-Chlorobenzoic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong bases. | | Fire Hazard | Flash point data for 4-Chlorobenzoic acid are not available; however, 4-Chlorobenzoic acid is probably combustible. | | Purification Methods | Purify it as for m-chlorobenzoic acid. It has also been crystallised from hot water, and from EtOH. [Beilstein 9 IV 973.] |
| 4-Chlorobenzoic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|