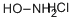| Description | Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is a reducing agent that is routinely used for the deacetylation of SATA to form free sulfhydryls (Figure 1), for cleavage of protein cross‐linkers that contain carbonyl groups (i.e. EGS) and for mutagenesis of plasmid DNA.Hydroxylamine converts aldehydes and ketones (carbonyls) to their oxime derivative in weak bases, therefore cross‐linkers and other compounds with carbonyl groups are cleavable with Hydroxylamine hydrochloride.SATA and SATP are modification reagents that add a sulfhydryl group to primary amines on biomolecules. The initial modification results in the addition of an acetyl‐protected sulfur enabling storage of the biomolecule. To generate a free sulfhydryl the biomolecule is treated with hydroxylamine to remove the protecting acetyl group (see figure).EGS and sulfo‐EGS are homobifunctional, succinimidyl ester, amine reactive crosslinkers that are resistant to cleavage by denaturants used in SDS‐PAGE conditions, but may be cleaved with hydroxylamine. |
| Chemical Properties | Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is an inorganic substance, a colorless crystalline, easily deliquescence, white chemical substance, mainly used as a reducing agent and an imaging agent, used in the preparation of oximes in organic synthesis, and also used in the synthesis of anticancer drugs (hydroxylamine hydrochloride). urea), sulfonamides (trimoxazole) and pesticides (methomyl). It has strong hygroscopicity and will decompose when it is damped above 151℃. At 17°C, 83.8g can be dissolved in 100g of water. This product is highly toxic and irritating to the skin. The production equipment should be sealed to prevent running, running, dripping and leaking, and operators should wear protective equipment. When splashed on the skin, rinse with plenty of water. |
| Physical properties | Colorless monoclinic crystals; hygroscopic; decomposes slowly in moist air;density 1.67 g/cm3at 17°C; melts at 151°C (decomposes); highly soluble inwater (84g/100g at 20°C); soluble in lower alcohols and glycols; pH of 0.1molar solution 3.4. |
| Uses | Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is a monomoamine oxidase inhibitor. It is used to prepare oximes and hydroxmic acids in organic synthesis. It acts as a copolymerization inhibitor. It can be used to remove bromine and polybromide from a solution during extraction of lignin from lignocellulosic biomass. It is key starting material for the preparation of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. It plays a vital role in rubber and plastic industries as an antioxidant, a vulcanization accelerator and a radical scavenger. It is also used as a color stabilizer and emulsion additive in color films. |
| Definition | ChEBI: Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is an organic molecular entity. It is a colorless inorganic compound (HONH2) used in organic synthesis and as a reducing agent, due to its ability to donate nitric oxide. |
| Preparation | Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is prepared by electrolytic reduction of ammonium chloride. Or by the action of nitromethane with hydrochloric acid and water to obtain hydroxylamine hydrochloride. |
| Biotechnological Applications | Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is a strong reducing agent that is useful in biochemical crosslinking applications, including the deacetylation of SATA and chemical cleavage of EGS and Sulfo-EGS. Hydroxylamine converts carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) to their oxime derivatives in the presence of a weak base. Therefore, crosslinkers and other compounds that contain a carbonyl within their structure are cleavable with hydroxylamine•HCl.
EGS and its water-soluble analog, Sulfo-EGS, are homobifunctional, succinimidyl ester, amine-reactive crosslinkers useful for covalent stabilization of polypeptide multimers and protein:protein interactions. Unlike disulfidecontaining crosslinkers, EGS and Sulfo-EGS will not cleave by reducing SDS-PAGE conditions but may be cleaved when necessary with hydroxylamine.
SATA and SATP are modification reagents for addition of sulfhydryl groups to proteins and other molecules containing primary amines. Such sulfhydryl addition is an important step in one popular method for preparing protein conjugates such as antibodies with horseradish peroxidase enzyme. The initial modification results in addition of an acetyl-protected sulfur, enabling storage of the modified protein; to make the sulfur available as a sulhydryl group (-SH) for the final conjugation reaction, hydroxylamine is used to remove the protecting acetyl group.
Hydroxylamine•HCl is more stable to oxidation than the free base form of hydroxylamine; nevertheless, always prepare hydroxylamine solutions immediately before use and store the product desiccated. Hydroxylamine•HCl is soluble in polar solvents such as water, ethanol, methanol, glycerol and propylene glycol. |
| General Description | Hydroxylamine hydrochloride appears as colorless or off-white crystalline solid. pH (0.1 molar aqueous solution) 3.4. pH (0.2 molar aqueous solution) 3.2. (NTP, 1992) |
| Air & Water Reactions | Hygroscopic. Sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. Water soluble. Reacts slowly with water. |
| Reactivity Profile | A powerful reducing agent. Reacts with bases and oxidizing agents. |
| Hazard | Toxic by ingestion, strong irritant to tissue. |
| Fire Hazard | Flash point data for Hydroxylamine hydrochloride are not available; however, Hydroxylamine hydrochloride is probably combustible. |
| Flammability and Explosibility | Notclassified |
| Biochem/physiol Actions | MAO inhibitor; inhibits platelet aggregation. |
| Contact allergens | Hydroxylamine and its salts are used in various
branches of industry, as reducing agents in color film
developers or as reagents in laboratories. |
| Purification Methods | Crystallise the salt from aqueous75% ethanol or boiling methanol, and dry it under vacuum over CaSO4 or P2O5. It has also been dissolved in a minimum of water and saturated with HCl; after three such crystallisations, it is dried under a vacuum over CaCl2 and NaOH. Its solubility at 20o is 85% in H2O, 6% in EtOH and 12% in MeOH. [Hurd Inorg Synth I 87 1939, Semon in Org Synth Coll Vol I 318 1941.] |